Exception
개요
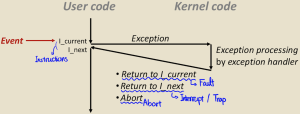
Exception이란 특정 이벤트가 발생함에 따라 OS kernel로 Control을 이동시키는 것을 의미한다. 이때 exception이 발생하면 커널[1]에서 exception handler를 통해서 이를 처리한다.
- 예시: 0나누기 / 오버플로우 / page fault[2] / I/O request completion / Ctrl - C
또한 Exception table이란 예외 발생시 해당 예외를 처리하는 Exception Handler의 주소를 저장하는 데이터 구조를 의미한다. 각각의 Exception은 고유한 예외 코드 K를 가지고 있으며, exception handler K는 해당 예외가 발생시 Exception Table에 저장된 주소를 통해 호출된다.
종류
| Class | Cause | Async/sync | Return behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interrupt | Signal from I/O Device | Async | Always returns to next instruction |
| Trap | Intentional exception | Sync | Always returns to next instruction |
| Fault | Potentially recoverable error | Sync | Might returns to current instruction |
| Abort | Non recoverable error | Sync | Never returns |
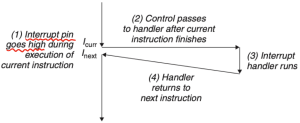
Interrupts (Asynchronous Exceptions)
Interrupts는 프로세서 외부에서 발생하는 이벤트에 의해 발생한다.[3]
CPU에는 물리적인 Interrupt Pin이 따로 존재하며, 해당 핀의 신호가 0 ->1로 바뀌면 인터럽트를 감지한다. 이를 Interrupt Handler가 처리하고 다시 next instruction으로 돌아간다.
Synchronous Exception
instruction을 실행시킴으로서 발생한 결과에 의한 이벤트에 의해서 발생하기 때문에 동기적으로 처리된다.
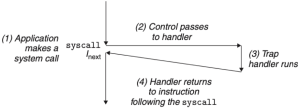
Traps
Trap은 CPU가 할 수 없는 작업을 OS에 넘겨주는 Exception으로, 의도적으로 발생한다. System Call이 Trap의 대표적인 한 종류이다.
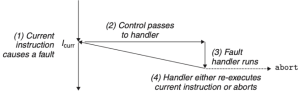
Faults
Fault는 비의도적이지만 복구가능할 수도 있는 오류이다. Handler를 실행한 후 문제의(current) instruction을 재실행하거나 중단한다.
- 예시: page faults(recoverable), protection fault(unrecovable)
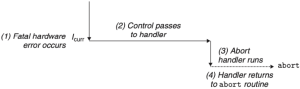
Aborts
Abort는 비의도적이고 복구도 불가능한 오류이며, 현재의 프로그램을 중단한다.
- 예시: illegal instruction, parity error, machine check